Custom Metal Stamping Services
Metal Stamping Manufacturing & Metal Parts Customization Supplier
What is metal stamping?
Metal stampings, also known as metal pressings, are a manufacturing process where flat metal sheets are formed into desired shapes through the use of specialized stamping dies and mechanical or hydraulic presses. This process is ideal for producing large quantities of complex, high-precision metal components with consistent quality and cost-efficiency. Metal stampings find extensive applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and appliances, providing solutions for a wide range of functional and structural requirements.
Advanced Equipment and Technology: We have invested in state-of-the-art metal stamping equipment and technology, including high-speed presses, multi-station dies, and automated production lines. The utilization of these equipment and technologies allows us to produce metal stampings at higher speeds and with greater efficiency.
Multi-Station Stamping Technology: We employ multi-station stamping technology, which enables multiple operations such as cutting, bending, forming, and piercing to be performed simultaneously on a single press. This technology not only improves production efficiency but also reduces the handling and movement of components, resulting in lower production costs.
Quality Assurance and Certification: We are committed to delivering high-quality metal stampings and hold ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certification for our quality management system. We implement strict quality control measures throughout the production process, including material inspection, process control, finished product testing, and validation, to ensure that each product meets customer requirements and standards.
High Precision and Consistency: We strictly control the process parameters and quality requirements of each production step to ensure the precision and consistency of every metal stamping. We utilize advanced measurement equipment and quality control tools for inspection and validation to ensure that each product meets the specified requirements.
Material Selection and Optimization: We collaborate with suppliers to select high-quality metal materials and optimize them based on customer requirements. Through proper material selection and optimization, we enhance the strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance of the products to meet various application needs.
Engineering Support and Collaboration: We have a professional engineering team that works closely with customers, providing technical support and solutions. We offer expertise in product design, process optimization, and cost control, assisting customers in achieving the best metal stamping solutions.
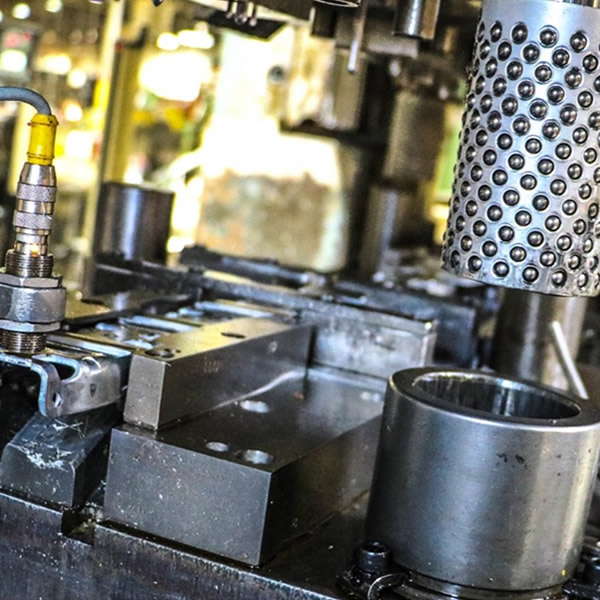

Custom Precision Metal Stampings for Global Industries
We specialize in custom metal stampings using materials like copper, brass, stainless steel, and steel alloys. This advanced technique enables us to fabricate a wide array of metal stamped components, varying in shape, size, and complexity, while reducing lead times and production costs. Our expertise serves diverse industries worldwide, delivering premium metal stamped parts.
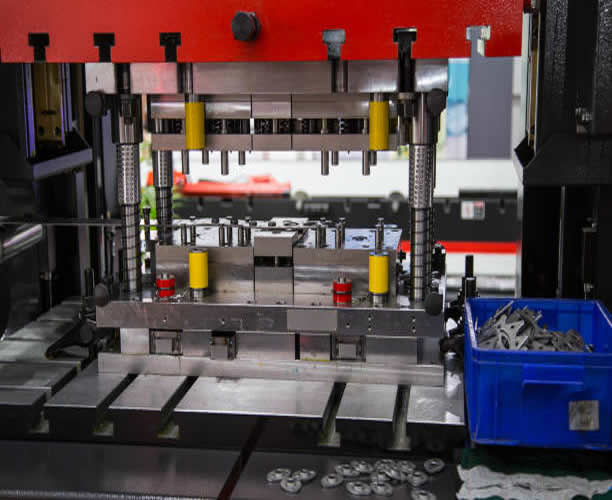

Trusted Custom Metal Stamping Solutions
Irrespective of the industry or specific product, we tailor our metal stamping solutions to precisely match the unique requirements and specifications of our esteemed clients. Our unwavering dedication to excellence ensures that every metal stamped component we produce upholds the highest standards of quality, precision, and reliability. When it comes to dependable metal stamping solutions, we are the preferred partner you can trust.
Our Metal Stamping Services & Capabilities:
We provide a variety of tooling services, including:
- Progressive Die Stamping
- Compound Die Stamping
- Transfer Die Stamping
- Punching
- Blanking
- Coining
- Embossing
- Flanging
- Bending
Equipment
Multiple presses with various shapes and sizes
From 5 to 300 tons
Multiple openings, beds, strokes, and speeds
Latest technology feeders to handle material of any weight
Capabilities
Stainless steel between 7 and 30 gauge
Tolerances to 0.05mm
Single and progressive dies
State-of-the-art die and tool shop with EDM capabilities
Our Metal Stamping Process Technologies:
Tool and Die Design: The design and engineering of precision tooling and dies are essential for metal stamping operations. These tools are customized to the specific part design and enable the shaping and cutting of the metal sheets.
Blanking: Blanking is the process of cutting the metal sheet into the desired shape using a die and a punch. This step removes the excess material from the sheet and prepares it for further forming operations.
Bending: Bending is the process of deforming the metal sheet using a punch and die to create angles, curves, or complex shapes. It requires precise control of the bending force, angle, and depth to achieve the desired shape.
Forming: Forming involves shaping the metal sheet using a combination of punches, dies, and other tools to create features such as embossing, ribbing, or flanging. It allows for the creation of intricate and functional designs.
Piercing: Piercing is the process of creating holes or openings in the metal sheet using a punch and die. This can be done to accommodate fasteners, ventilation, or other functional requirements.
Coining: Coining is a precision forming process that applies high pressure to the metal sheet to create tight tolerances, smooth surfaces, and sharp edges. It is often used to achieve high-quality finishes and precise dimensional control.
Assembly: Metal stampings may require additional assembly processes such as welding, riveting, or fastening to join multiple stamped components together or to other parts.
These various process technologies are combined and customized based on the specific requirements of the metal stamping project to achieve the desired shape, dimensions, and functionality of the final stamped component.
Sheet Metal Design Guidelines
During the metal stamping design process, it's essential to consider the following guidelines:
Holes: The hole diameter should be at least 1.2 times the material thickness. For high-tensile materials like stainless steel alloys, the minimum hole diameter should be at least two times the material thickness.
Edge to Holes: Maintain a distance of two stock thicknesses between holes and the edge. For oblong holes shorter than 10 material thicknesses, the edge-to-hole spacing should be two times the material thickness. For longer oblong holes, the spacing should be four times the material thickness or more to avoid bulging.
Hole to Form: To prevent hole deformation when forming a bend close to a hole, the spacing should be the bend radius plus 2.5 times the material thickness. If the hole's diameter or width is less than 2.5mm, the distance should be a minimum of twice the material's thickness plus the bend radius. For larger holes, the spacing should be the bend radius plus 2.5 times the material thickness.
Slot to Form: When bending near long slots, maintain a spacing of the bend radius plus a minimum of four times the material thickness to prevent deformation.
Notches & Tabs: Ensure notches and tabs are at least 1.5 times the material thickness to prevent breakage during stamping.
Corners: For easy manufacturing, the radius of the punch and die for forming corners should be at least four times the material thickness. For materials 1.5mm or thinner, avoid sharp corners.
Squareness: Stamping to form a square, 90° angle allows for normal variation of plus or minus 1 degree.
Flatness: Avoid over-specifying flatness, as it may require costly secondary operations. Specify flatness requirements reasonably.
L-Shaped Parts: Include a bend relief notch in L-shaped parts to avoid fractures and cracks.
Grain Direction: Consider grain direction, especially for hard stocks. Avoid having the bend line of sharp V-bends parallel to the grain direction to prevent cracking. A larger bend radius may also be needed for harder materials.
Burrs: Burrs can occur during stamping and can reach heights of up to 10% of the material thickness. Minimize burr severity by avoiding complex cutouts and sharp corners where possible. Note burr direction in the design to account for them during the metal stamping process.
Shapes: Simple shapes like rounds and squares with sufficient corner radii are easier to draw in stamping. Complex shapes or irregular shapes may increase the difficulty and production cost.
Feature Distortion: Be mindful of distortion when holes and slots are too close to forms, edges, or each other, especially in drawn parts. Account for potential deformation in the design process.
By following these guidelines, you can improve the efficiency and quality of the metal stamping process and reduce the likelihood of defects and issues during manufacturing.
Metal Stamping Materials
| Material | Grades Available | Key Properties | Common Applications |
| Steel | CRS (Cold Rolled Steel) | Excellent formability and versatility | Cold forming applications |
| 1008 | |||
| 1010 | |||
| 1018 | |||
| Stainless Steel | 301 | Exceptional tensile strength | Structural components, springs |
| 304 | Enhanced performance and corrosion resistance at higher temperatures | Food processing equipment, plumbing | |
| 316/316L | Best corrosion resistance (higher cost) | Marine environments, medical devices | |
| Copper | C110 | Excellent electrical conductivity, easy formability | Electrical wiring, conductors |
| Brass | Brass 230 (85/15) | Highly formable, corrosion-resistant | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors |
| Brass 260 (70/30) | Musical instruments, decorative items |
Additionally, we have the capability to accommodate other sheet metal materials upon request. Please don't hesitate to contact our experts to discuss your specific material requirements.
The Tolerance of Metal Stampings
The tolerance range for metal stampings typically varies based on specific design requirements and application needs. Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation in dimensions during the manufacturing process to ensure the quality and functional requirements of the parts.
In metal stampings, controlling tolerances is crucial to maintaining product quality and performance. Here are some common examples of tolerance ranges:
Dimensional Tolerance: Dimensional tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions such as length, width, thickness, etc., of the parts. For example, for a part with a length of 100mm, the dimensional tolerance can be ±0.1mm, indicating an allowable deviation range of 99.9mm to 100.1mm.
Flatness Tolerance: Flatness tolerance measures the levelness of the part's surface. It describes the maximum distance between the part surface and an ideal plane. For example, the flatness tolerance can be 0.1mm, indicating a maximum distance of 0.1mm between the part surface and the ideal plane.
Parallelism Tolerance: Parallelism tolerance describes the deviation between parallel surfaces of the part. It measures the maximum difference in distance between the parallel surfaces. For example, the parallelism tolerance can be 0.05mm, indicating a maximum distance difference between the parallel surfaces of 0.05mm.
Roundness Tolerance: Roundness tolerance measures the roundness deviation of circular parts. It describes the maximum distance between the curve around the circular part and an ideal circle. For example, the roundness tolerance can be 0.03mm, indicating a maximum distance between the curve around the circular part and the ideal circle of 0.03mm.
These tolerance ranges are just examples, and actual tolerances should be determined based on specific design requirements and application needs. During the design process, factors such as part functionality, assembly requirements, and manufacturing feasibility need to be considered to determine the appropriate tolerance ranges.
Applications of Metal Stamping Dies:
Metal stamping is a forming process that shapes and molds sheet metal workpieces between a punch press and a die. Metal stamping dies are tools attached to the stamping press. They manipulate the workpiece and provide support for its formation. Unlike other bending processes, stamping relieves internal stresses in the metal, preventing post-stamping springback or deformation.
Metal stamping finds extensive use in various applications and is a versatile process capable of high-volume production. Custom metal stamping dies can be configured for a wide range of applications, including:
Our comprehensive Metal stampings lineup main including:
- Electronic Control Connectors
- Electronic Control Brackets
- Circuit Board Heat Sinks
- Circuit Board Contacts
- Metal Diaphragms for Audio Speakers
- Stainless Steel Shielding Components
- Power Adapter Plugs
- Gold and Silver-Plated Aviation Connectors
- Headphone Speaker Brackets
- Fuse Tube Clips
Due to the repeatability, durability, and precision of metal stamped components, metal stamping is an ideal choice for performance-critical industries such as automotive and medical.
Our Quality Control for Metal Stamping
Quality control is a critical aspect of our metal stamping service, and we take utmost care to ensure that every product we manufacture meets the highest standards of quality and precision. Our quality control process is rigorous and covers various stages of production, from initial design to final inspection. Here's how we implement quality control in our metal stamping service:
Design Review: We start by conducting a thorough design review to ensure that the product design meets the required specifications and standards. Our team of experienced engineers examines the design for any potential issues or improvements that can be made to enhance product performance.
Material Selection: We use only high-quality materials sourced from reputable suppliers. Our materials undergo stringent testing to ensure they meet the necessary mechanical and chemical properties for the specific application.
Advanced Machinery and Technology: We utilize state-of-the-art stamping equipment and technology in our manufacturing process. Our machines are regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure accurate and consistent results.
In-Process Inspection: Throughout the stamping process, we conduct in-process inspections to monitor the quality of each component as it is being manufactured. This allows us to detect and address any deviations or defects promptly.
Dimensional Accuracy: We employ precision measuring instruments to verify the dimensional accuracy of each stamped part. This ensures that the final product conforms to the required specifications.
Surface Finish and Coatings: We pay close attention to the surface finish of the stamped components. Depending on the application, we may apply various coatings or treatments to enhance durability and corrosion resistance.
Final Inspection: Before shipping, each batch of stamped products undergoes a comprehensive final inspection. Our quality control team examines the parts for any defects, ensuring that they meet all customer requirements.
Traceability and Documentation: We maintain meticulous records of the entire production process, including material certifications, inspection reports, and other relevant documentation. This ensures full traceability and transparency in our quality control procedures.
Our commitment to quality control has earned us a reputation for delivering reliable and high-quality metal stamped components to our customers. We continuously strive for continuous improvement, investing in training, and upgrading our equipment to stay at the forefront of quality manufacturing.






